7 August 18:01

International
foto:shutterstock
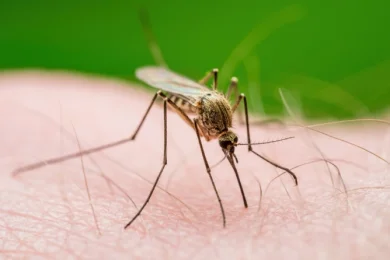
The Chikungunya outbreak in southern China has led to more than 7,700 confirmed infections, mostly in Foshan city. Authorities have implemented strict measures to limit the spread of the virus, including registering the identity of those who buy medicines and a self-monitoring period for travelers in Guangdong. Public criticism has intensified, comparing the restrictions to those during the COVID-19 pandemic. The virus, transmitted by the tiger mosquito, is a global threat, with confirmed cases in 119 countries. Climate change is contributing to its proliferation.